Barycentric coordinates
export barycentric_coordinates, barycentric_coordinates!, barycentric_interpolate
export MeanValueGeneralized barycentric coordinates are a generalization of barycentric coordinates, which are typically used in triangles, to arbitrary polygons.
They provide a way to express a point within a polygon as a weighted average of the polygon's vertices.
In the case of a triangle, barycentric coordinates are a set of three numbers
For a polygon with
As with the triangle case, the weights sum to 1, and each is non-negative.
Example
This example was taken from this page of CGAL's documentation.
import GeometryOps as GO, GeoInterface as GI
using CairoMakie # plotting
# Define a polygon
polygon_points = [
(0.03, 0.05, 0.00), (0.07, 0.04, 0.02), (0.10, 0.04, 0.04),
(0.14, 0.04, 0.06), (0.17, 0.07, 0.08), (0.20, 0.09, 0.10),
(0.22, 0.11, 0.12), (0.25, 0.11, 0.14), (0.27, 0.10, 0.16),
(0.30, 0.07, 0.18), (0.31, 0.04, 0.20), (0.34, 0.03, 0.22),
(0.37, 0.02, 0.24), (0.40, 0.03, 0.26), (0.42, 0.04, 0.28),
(0.44, 0.07, 0.30), (0.45, 0.10, 0.32), (0.46, 0.13, 0.34),
(0.46, 0.19, 0.36), (0.47, 0.26, 0.38), (0.47, 0.31, 0.40),
(0.47, 0.35, 0.42), (0.45, 0.37, 0.44), (0.41, 0.38, 0.46),
(0.38, 0.37, 0.48), (0.35, 0.36, 0.50), (0.32, 0.35, 0.52),
(0.30, 0.37, 0.54), (0.28, 0.39, 0.56), (0.25, 0.40, 0.58),
(0.23, 0.39, 0.60), (0.21, 0.37, 0.62), (0.21, 0.34, 0.64),
(0.23, 0.32, 0.66), (0.24, 0.29, 0.68), (0.27, 0.24, 0.70),
(0.29, 0.21, 0.72), (0.29, 0.18, 0.74), (0.26, 0.16, 0.76),
(0.24, 0.17, 0.78), (0.23, 0.19, 0.80), (0.24, 0.22, 0.82),
(0.24, 0.25, 0.84), (0.21, 0.26, 0.86), (0.17, 0.26, 0.88),
(0.12, 0.24, 0.90), (0.07, 0.20, 0.92), (0.03, 0.15, 0.94),
(0.01, 0.10, 0.97), (0.02, 0.07, 1.00)]
# Plot it!
# First, we'll plot the polygon using Makie's rendering:
f, a1, p1 = poly(
Point2.(GO.forcexy(polygon_points));
color = last.(polygon_points),
colormap = cgrad(:jet, 18; categorical = true),
axis = (;
type = Axis, aspect = DataAspect(), title = "Makie mesh based polygon rendering", subtitle = "CairoMakie"
),
figure = (; size = (800, 400),)
)
hidedecorations!(a1)
ext = GO.Extents.Extent(X = (0, 0.5), Y = (0, 0.42))
a2 = Axis(
f[1, 2],
aspect = DataAspect(),
title = "Barycentric coordinate based polygon rendering", subtitle = "GeometryOps",
limits = (ext.X, ext.Y)
)
hidedecorations!(a2)
p2box = poly!( # Now, we plot a cropping rectangle around the axis so we only show the polygon
a2,
GI.Polygon( # This is a rectangle with an internal hole shaped like the polygon.
[
Point2f[(ext.X[1], ext.Y[1]), (ext.X[2], ext.Y[1]), (ext.X[2], ext.Y[2]), (ext.X[1], ext.Y[2]), (ext.X[1], ext.Y[1])], # exterior
reverse(Point2f.(GO.forcexy(polygon_points))) # hole
]
); color = :white, xautolimits = false, yautolimits = false
)
cb = Colorbar(f[2, :], p1.plots[1]; vertical = false, flipaxis = true)
# Finally, we perform barycentric interpolation on a grid,
xrange = LinRange(ext.X..., 400)
yrange = LinRange(ext.Y..., 400)
@time mean_values = GO.barycentric_interpolate.(
(GO.MeanValue(),), # The barycentric coordinate algorithm (MeanValue is the only one for now)
(GI.Polygon(GI.LinearRing.([polygon_points])),), # The polygon
(last.(polygon_points,),), # The values per polygon point - can be anything which supports addition and division
tuple.(xrange, yrange') # The points at which to interpolate
)
# and render!
hm = heatmap!(a2, xrange, yrange, mean_values; colormap = p1.colormap, colorrange = p1.plots[1].colorrange[], xautolimits = false, yautolimits = false)
translate!(hm, 0, 0, -1) # translate the heatmap behind the cropping polygon!
f # finally, display the figure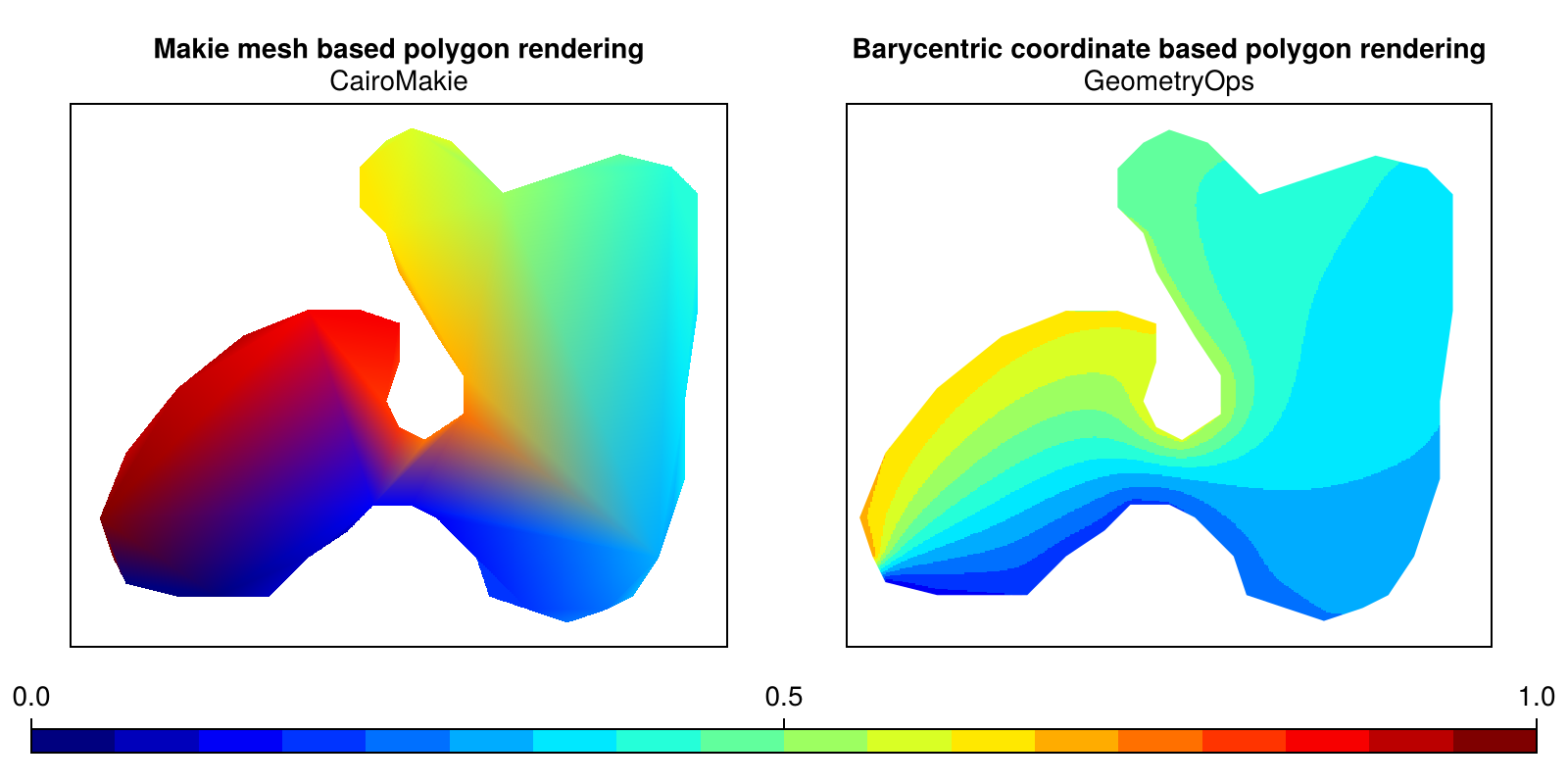
Barycentric-coordinate API
In some cases, we actually want barycentric interpolation, and have no interest in the coordinates themselves.
However, the coordinates can be useful for debugging, and when performing 3D rendering, multiple barycentric values (depth, uv) are needed for depth buffering.
"native Julia vector-like types with known size"
const _VecTypes = Union{Tuple{Vararg{T, N}}, StaticArrays.StaticArray{Tuple{N}, T, 1}} where {N, T}
"""
abstract type AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod
Abstract supertype for barycentric coordinate methods.
The subtypes may serve as dispatch types, or may cache
some information about the target polygon.
# API
The following methods must be implemented for all subtypes:
- `barycentric_coordinates!(λs::Vector{<: Real}, method::AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod, exterior::Vector{<: Point{2, T1}}, point::Point{2, T2})`
- `barycentric_interpolate(method::AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod, exterior::Vector{<: Point{2, T1}}, values::Vector{V}, point::Point{2, T2})::V`
- `barycentric_interpolate(method::AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod, exterior::Vector{<: Point{2, T1}}, interiors::Vector{<: Vector{<: Point{2, T1}}} values::Vector{V}, point::Point{2, T2})::V`
The rest of the methods will be implemented in terms of these, and have efficient dispatches for broadcasting.
"""
abstract type AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod endBase.@propagate_inbounds function barycentric_interpolate(method::AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod, polygon::Polygon{2, T1}, values::AbstractVector{V}, point::Point{2, T2}) where {T1 <: Real, T2 <: Real, V} exterior = decompose(Point{2, promote_type(T1, T2)}, polygon.exterior) if isempty(polygon.interiors) @boundscheck @assert length(values) == length(exterior) return barycentric_interpolate(method, exterior, values, point) else # the poly has interiors interiors = reverse.(decompose.((Point{2, promote_type(T1, T2)},), polygon.interiors)) @boundscheck @assert length(values) == length(exterior) + sum(length.(interiors)) return barycentric_interpolate(method, exterior, interiors, values, point) end end
3D polygons are considered to have their vertices in the XY plane, and the Z coordinate must represent some value. This is to say that the Z coordinate is interpreted as an M coordinate. Base.@propagate_inbounds function barycentric_interpolate(method::AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod, polygon::Polygon{3, T1}, point::Point{2, T2}) where {T1 <: Real, T2 <: Real} exterior_point3s = decompose(Point{3, promote_type(T1, T2)}, polygon.exterior) exterior_values = getindex.(exterior_point3s, 3) exterior_points = Point2f.(exterior_point3s) if isempty(polygon.interiors) return barycentric_interpolate(method, exterior_points, exterior_values, point) else # the poly has interiors interior_point3s = decompose.((Point{3, promote_type(T1, T2)},), polygon.interiors) interior_values = collect(Iterators.flatten((getindex.(point3s, 3) for point3s in interior_point3s))) interior_points = map(point3s -> Point2f.(point3s), interior_point3s) return barycentric_interpolate(method, exterior_points, interior_points, vcat(exterior_values, interior_values), point) end end
This method is the one which supports GeoInterface. """ barycentric_interpolate(method = MeanValue(), polygon, values::AbstractVector{V}, point)
Returns the interpolated value at point within polygon using the barycentric coordinate method method. values are the per-point values for the polygon which are to be interpolated.
Returns an object of type V.
Warning
Barycentric interpolation is currently defined only for 2-dimensional polygons. If you pass a 3-D polygon in, the Z coordinate will be used as per-vertex value to be interpolated (the M coordinate in GIS parlance).
"""
"""
weighted_mean(weight::Real, x1, x2)
Returns the weighted mean of `x1` and `x2`, where `weight` is the weight of `x1`.
Specifically, calculates `x1 * weight + x2 * (1 - weight)`.
!!! note
The idea for this method is that you can override this for custom types, like Color types, in extension modules.
"""
function weighted_mean(weight::WT, x1, x2) where {WT <: Real}
return muladd(x1, weight, x2 * (oneunit(WT) - weight))
end
"""
MeanValue() <: AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod
This method calculates barycentric coordinates using the mean value method.
# References
"""
struct MeanValue <: AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod
endBefore we go to the actual implementation, there are some quick and simple utility functions that we need to implement. These are mainly for convenience and code brevity.
"""
_det(s1::Point2{T1}, s2::Point2{T2}) where {T1 <: Real, T2 <: Real}
Returns the determinant of the matrix formed by `hcat`'ing two points `s1` and `s2`.
Specifically, this is:
```julia
s1[1] * s2[2] - s1[2] * s2[1]
```
"""
function _det(s1::_VecTypes{2, T1}, s2::_VecTypes{2, T2}) where {T1 <: Real, T2 <: Real}
return s1[1] * s2[2] - s1[2] * s2[1]
end
"""
t_value(sᵢ, sᵢ₊₁, rᵢ, rᵢ₊₁)
Returns the "T-value" as described in Hormann's presentation [^HormannPresentation] on how to calculate
the mean-value coordinate.
Here, `sᵢ` is the vector from vertex `vᵢ` to the point, and `rᵢ` is the norm (length) of `sᵢ`.
`s` must be `Point` and `r` must be real numbers.
```math
tᵢ = \\frac{\\mathrm{det}\\left(sᵢ, sᵢ₊₁\\right)}{rᵢ * rᵢ₊₁ + sᵢ ⋅ sᵢ₊₁}
```
[^HormannPresentation]: K. Hormann and N. Sukumar. Generalized Barycentric Coordinates in Computer Graphics and Computational Mechanics. Taylor & Fancis, CRC Press, 2017.
```
"""
function t_value(sᵢ::_VecTypes{N, T1}, sᵢ₊₁::_VecTypes{N, T1}, rᵢ::T2, rᵢ₊₁::T2) where {N, T1 <: Number, T2 <: Number}
return _det(sᵢ, sᵢ₊₁) / muladd(rᵢ, rᵢ₊₁, dot(sᵢ, sᵢ₊₁))
end
function barycentric_coordinates(alg::AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod, geom, in_point; normalize = true)
barycentric_coordinates(alg, GI.geomtrait(geom), geom, GI.geomtrait(in_point), in_point; normalize)
end
function barycentric_coordinates(alg::AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod, t1::GI.AbstractCurveTrait, geom, t2::GI.PointTrait, in_point; normalize = true)
λs = Vector{float(typeof(GI.x(in_point)))}(undef, GI.npoint(geom) - (GI.isclosed(geom) ? 1 : 0))
barycentric_coordinates!(λs, alg, t1, geom, t2, in_point; normalize)
return λs
end
function barycentric_coordinates!(λs::Vector{<: Real}, ::AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod, geom, in_point; normalize = true)
@boundscheck @assert GI.npoint(geom) >= 3
barycentric_coordinates!(λs, MeanValue(), GI.geomtrait(geom), geom, GI.geomtrait(in_point), in_point; normalize)
end
function barycentric_coordinates!(λs::Vector{<: Real}, ::MeanValue, ::GI.AbstractCurveTrait, ring, ::GI.PointTrait, in_point; normalize = true)
@boundscheck @assert length(λs) == GI.npoint(ring)
@boundscheck @assert GI.npoint(ring) >= 3
T = float(typeof(GI.x(in_point)))
point = _tuple_point(in_point, T)
n_points = GI.npoint(ring)
# Initialize counters and register variables
# Points - these are actually vectors from point to vertices
# polypoints[i-1], polypoints[i], polypoints[i+1]
sᵢ₋₁ = _tuple_point(GI.getpoint(ring, n_points), T) .- point
sᵢ = _tuple_point(GI.getpoint(ring, 1), T) .- point
sᵢ₊₁ = _tuple_point(GI.getpoint(ring, 2), T) .- point
# radius / Euclidean distance between points.
rᵢ₋₁ = norm(sᵢ₋₁)
rᵢ = norm(sᵢ )
rᵢ₊₁ = norm(sᵢ₊₁)
# Perform the first computation explicitly, so we can cut down on
# a mod in the loop.
λs[1] = (t_value(sᵢ₋₁, sᵢ, rᵢ₋₁, rᵢ) + t_value(sᵢ, sᵢ₊₁, rᵢ, rᵢ₊₁)) / rᵢ
# Loop through the rest of the vertices, compute, store in λs
for i in 2:n_points
# Increment counters + set variables
sᵢ₋₁ = sᵢ
sᵢ = sᵢ₊₁
sᵢ₊₁ = _tuple_point(GI.getpoint(ring, mod1(i+1, n_points)), T) .- point
rᵢ₋₁ = rᵢ
rᵢ = rᵢ₊₁
rᵢ₊₁ = norm(sᵢ₊₁) # radius / Euclidean distance between points.
λs[i] = (t_value(sᵢ₋₁, sᵢ, rᵢ₋₁, rᵢ) + t_value(sᵢ, sᵢ₊₁, rᵢ, rᵢ₊₁)) / rᵢ
end
# Normalize λs to the 1-norm (sum=1)
normalize && (λs ./= sum(λs))
return λs
endfunction barycentric_coordinates(::MeanValue, polypoints::NTuple{N, Point{2, T2}}, point::Point{2, T1},) where {N, T1, T2}
## Initialize counters and register variables
## Points - these are actually vectors from point to vertices
## polypoints[i-1], polypoints[i], polypoints[i+1]
sᵢ₋₁ = polypoints[end] - point
sᵢ = polypoints[begin] - point
sᵢ₊₁ = polypoints[begin+1] - point
## radius / Euclidean distance between points.
rᵢ₋₁ = norm(sᵢ₋₁)
rᵢ = norm(sᵢ )
rᵢ₊₁ = norm(sᵢ₊₁)
λ₁ = (t_value(sᵢ₋₁, sᵢ, rᵢ₋₁, rᵢ) + t_value(sᵢ, sᵢ₊₁, rᵢ, rᵢ₊₁)) / rᵢ
λs = ntuple(N) do i
if i == 1
return λ₁
end
## Increment counters + set variables
sᵢ₋₁ = sᵢ
sᵢ = sᵢ₊₁
sᵢ₊₁ = polypoints[mod1(i+1, N)] - point
rᵢ₋₁ = rᵢ
rᵢ = rᵢ₊₁
rᵢ₊₁ = norm(sᵢ₊₁) # radius / Euclidean distance between points.
return (t_value(sᵢ₋₁, sᵢ, rᵢ₋₁, rᵢ) + t_value(sᵢ, sᵢ₊₁, rᵢ, rᵢ₊₁)) / rᵢ
end
∑λ = sum(λs)
return ntuple(N) do i
λs[i] / ∑λ
end
endfunction barycentric_interpolate(alg::AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod, geom, values::AbstractVector, point)
barycentric_interpolate(alg, GI.geomtrait(geom), geom, values, GI.geomtrait(point), point)
endThis performs an inplace accumulation, using less memory and is faster. That's particularly good if you are using a polygon with a large number of points...
function barycentric_interpolate(::MeanValue, ::GI.AbstractCurveTrait, ring, values::AbstractVector{V}, ::GI.PointTrait, point; normalize = true) where V
@boundscheck @assert length(values) == GI.npoint(ring)
@boundscheck @assert GI.npoint(ring) >= 3
T = float(typeof(GI.x(point)))
point = _tuple_point(point, T)
n_points = GI.npoint(ring) - (GI.isclosed(ring) ? 1 : 0) # do not iterate over the "closing" / last point, which is duplicated.
# Initialize counters and register variables
# Points - these are actually vectors from point to vertices
# polypoints[i-1], polypoints[i], polypoints[i+1]
sᵢ₋₁ = _tuple_point(GI.getpoint(ring, n_points), T) .- point
sᵢ = _tuple_point(GI.getpoint(ring, 1), T) .- point
sᵢ₊₁ = _tuple_point(GI.getpoint(ring, 2), T) .- point
# radius / Euclidean distance between points.
rᵢ₋₁ = norm(sᵢ₋₁)
rᵢ = norm(sᵢ )
rᵢ₊₁ = norm(sᵢ₊₁)
# Now, we set the interpolated value to the first point's value, multiplied
# by the weight computed relative to the first point in the polygon.
wᵢ = (t_value(sᵢ₋₁, sᵢ, rᵢ₋₁, rᵢ) + t_value(sᵢ, sᵢ₊₁, rᵢ, rᵢ₊₁)) / rᵢ
wₜₒₜ = wᵢ
interpolated_value = values[begin] * wᵢ
for i in 2:n_points
# Increment counters + set variables
sᵢ₋₁ = sᵢ
sᵢ = sᵢ₊₁
sᵢ₊₁ = _tuple_point(GI.getpoint(ring, mod1(i+1, n_points)), T) .- point
rᵢ₋₁ = rᵢ
rᵢ = rᵢ₊₁
rᵢ₊₁ = norm(sᵢ₊₁)
# Now, we calculate the weight:
wᵢ = (t_value(sᵢ₋₁, sᵢ, rᵢ₋₁, rᵢ) + t_value(sᵢ, sᵢ₊₁, rᵢ, rᵢ₊₁)) / rᵢ
# perform a weighted sum with the interpolated value:
interpolated_value += values[i] * wᵢ
# and add the weight to the total weight accumulator.
wₜₒₜ += wᵢ
end
# Return the normalized interpolated value.
if normalize
return interpolated_value / wₜₒₜ
else
return (interpolated_value, wₜₒₜ)
end
endWhen you have holes, then you have to be careful about the order you iterate around points.
Specifically, you have to iterate around each linear ring separately and ensure there are no degenerate/repeated points at the start and end!
function barycentric_interpolate(alg::AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod, ::GI.PolygonTrait, polygon, values::AbstractVector{V}, ::GI.PointTrait, point; normalize = true) where V <: Number
# @boundscheck @assert length(values) == (length(exterior) + isempty(interiors) ? 0 : sum(length.(interiors)))
# @boundscheck @assert length(exterior) >= 3
@boundscheck @assert length(values) == GI.npoint(polygon)
@boundscheck @assert all(>=(3), (GI.npoint(ring) for ring in GI.getring(polygon)))
if GI.nring(polygon) == 1
return barycentric_interpolate(alg, GI.LinearRingTrait(), GI.getexterior(polygon), values, GI.PointTrait(), point; normalize)
else
lazy_ring_n_points = Iterators.map(GI.npoint, GI.getring(polygon))
lazy_cumulative_npoints = Iterators.accumulate(+, lazy_ring_n_points)
value_idxs_per_ring = zip(Iterators.flatten((1, Iterators.map(Base.Fix2(+, 1), Iterators.take(lazy_cumulative_npoints, GI.nring(polygon) - 1)))), lazy_cumulative_npoints)
itps_and_weights = Iterators.map(GI.getring(polygon), value_idxs_per_ring) do ring, (start_idx, end_idx)
barycentric_interpolate(alg, GI.LinearRingTrait(), ring, view(values, start_idx:end_idx), GI.PointTrait(), point; normalize = false)
end
(final_i, final_w) = reduce(itps_and_weights; init = (0.0, 0.0)) do (i1, w1), (i2, w2)
return (i1 + i2, w1 + w2)
end
return normalize ? final_i / final_w : (final_i, final_w)
end
endTODO: not implemented yet
struct Wachspress <: AbstractBarycentricCoordinateMethod end
This page was generated using Literate.jl.