Distance
export distance, signed_distanceWhat is distance? What is signed distance?
Distance is the distance of a point to another geometry. This is always a positive number. If a point is inside of geometry, so on a curve or inside of a polygon, the distance will be zero. Signed distance is mainly used for polygons and multipolygons. If a point is outside of a geometry, signed distance has the same value as distance. However, points within the geometry have a negative distance representing the distance of a point to the closest boundary. Therefore, for all "non-filled" geometries, like curves, the distance will either be positive or 0.
To provide an example, consider this rectangle:
import GeometryOps as GO
import GeoInterface as GI
using CairoMakie
rect = GI.Polygon([[(0,0), (0,1), (1,1), (1,0), (0, 0)]])
point_in = (0.5, 0.5)
point_out = (0.5, 1.5)
f, a, p = poly(collect(GI.getpoint(rect)); axis = (; aspect = DataAspect()))
scatter!(GI.x(point_in), GI.y(point_in); color = :red)
scatter!(GI.x(point_out), GI.y(point_out); color = :orange)
f
This is clearly a rectangle with one point inside and one point outside. The points are both an equal distance to the polygon. The distance to point_in is negative while the distance to point_out is positive.
(
GO.distance(point_in, rect), # == 0
GO.signed_distance(point_in, rect), # < 0
GO.signed_distance(point_out, rect) # > 0
)(0.0, -0.5, 0.5)Consider also a heatmap of signed distances around this object:
xrange = yrange = LinRange(-0.5, 1.5, 300)
f, a, p = heatmap(xrange, yrange, GO.signed_distance.(tuple.(xrange, yrange'), (rect,)); colormap = :RdBu, colorrange = (-0.75, 0.75))
a.aspect = DataAspect(); Colorbar(f[1, 2], p, label = "Signed distance"); lines!(a, rect); f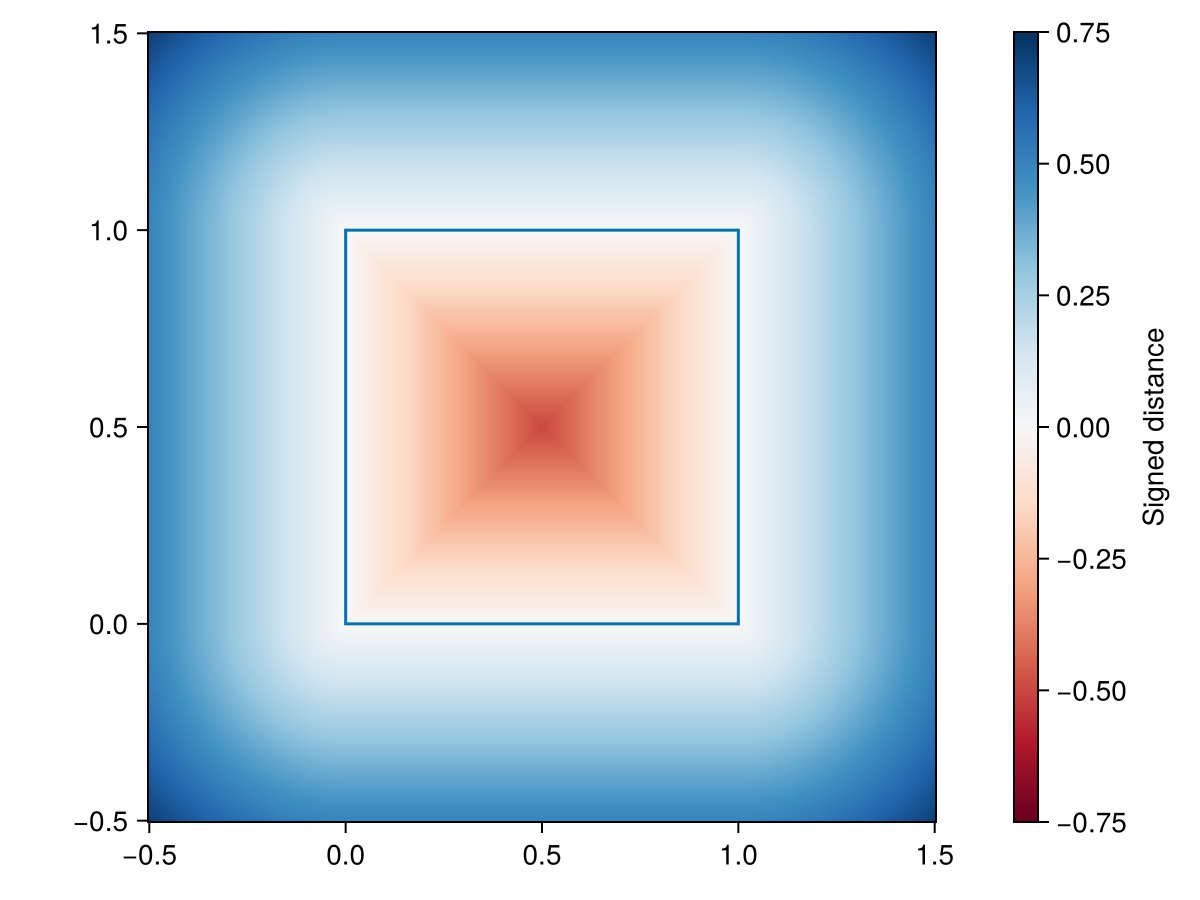
Implementation
This is the GeoInterface-compatible implementation. First, we implement a wrapper method that dispatches to the correct implementation based on the geometry trait. This is also used in the implementation, since it's a lot less work!
Distance and signed distance are only implemented for points to other geometries right now. This could be extended to include distance from other geometries in the future.
The distance calculated is the Euclidean distance using the Pythagorean theorem. Also note that singed_distance only makes sense for "filled-in" shapes, like polygons, so it isn't implemented for curves.
const _DISTANCE_TARGETS = TraitTarget{Union{GI.AbstractPolygonTrait,GI.LineStringTrait,GI.LinearRingTrait,GI.LineTrait,GI.PointTrait}}()
"""
distance(point, geom, ::Type{T} = Float64)::T
Calculates the distance from the geometry `g1` to the `point`. The distance
will always be positive or zero.
The method will differ based on the type of the geometry provided:
- The distance from a point to a point is just the Euclidean distance
between the points.
- The distance from a point to a line is the minimum distance from the point
to the closest point on the given line.
- The distance from a point to a linestring is the minimum distance from the
point to the closest segment of the linestring.
- The distance from a point to a linear ring is the minimum distance from
the point to the closest segment of the linear ring.
- The distance from a point to a polygon is zero if the point is within the
polygon and otherwise is the minimum distance from the point to an edge of
the polygon. This includes edges created by holes.
- The distance from a point to a multigeometry or a geometry collection is
the minimum distance between the point and any of the sub-geometries.
Result will be of type T, where T is an optional argument with a default value
of Float64.
"""
function distance(
geom1, geom2, ::Type{T} = Float64; threaded=false
) where T<:AbstractFloat
distance(GI.trait(geom1), geom1, GI.trait(geom2), geom2, T; threaded)
end
function distance(
trait1, geom, trait2::GI.PointTrait, point, ::Type{T} = Float64;
threaded=false
) where T<:AbstractFloat
distance(trait2, point, trait1, geom, T) # Swap order
end
function distance(
trait1::GI.PointTrait, point, trait2, geom, ::Type{T} = Float64;
threaded=false
) where T<:AbstractFloat
applyreduce(min, _DISTANCE_TARGETS, geom; threaded, init=typemax(T)) do g
_distance(T, trait1, point, GI.trait(g), g)
end
endNeeded for method ambiguity
function distance(
trait1::GI.PointTrait, point1, trait2::GI.PointTrait, point2, ::Type{T} = Float64;
threaded=false
) where T<:AbstractFloat
_distance(T, trait1, point1, trait2, point2)
endPoint-Point, Point-Line, Point-LineString, Point-LinearRing
_distance(::Type{T}, ::GI.PointTrait, point, ::GI.PointTrait, geom) where T =
_euclid_distance(T, point, geom)
_distance(::Type{T}, ::GI.PointTrait, point, ::GI.LineTrait, geom) where T =
_distance_line(T, point, GI.getpoint(geom, 1), GI.getpoint(geom, 2))
_distance(::Type{T}, ::GI.PointTrait, point, ::GI.LineStringTrait, geom) where T =
_distance_curve(T, point, geom; close_curve = false)
_distance(::Type{T}, ::GI.PointTrait, point, ::GI.LinearRingTrait, geom) where T =
_distance_curve(T, point, geom; close_curve = true)Point-Polygon
function _distance(::Type{T}, ::GI.PointTrait, point, ::GI.PolygonTrait, geom) where T
within(point, geom) && return zero(T)
return _distance_polygon(T, point, geom)
end
function distance(m::Manifold, geom1, geom2, ::Type{T} = Float64; kwargs...) where T <: AbstractFloat
distance(m, GI.trait(geom1), geom1, GI.trait(geom2), geom2, T; kwargs...)
end
function distance(
m::Manifold, trait1, geom, trait2::GI.PointTrait, point, ::Type{T} = Float64;
threaded=false
) where T<:AbstractFloat
distance(m, trait2, point, trait1, geom, T) # Swap order
end
function distance(
m::Manifold, trait1::GI.PointTrait, point, trait2, geom, ::Type{T} = Float64;
threaded=false
) where T<:AbstractFloat
applyreduce(min, _DISTANCE_TARGETS, geom; threaded, init=typemax(T)) do g
_distance(m, T, trait1, point, GI.trait(g), g)
end
endNeeded for method ambiguity
function distance(
m::Manifold, trait1::GI.PointTrait, point1, trait2::GI.PointTrait, point2, ::Type{T} = Float64;
threaded=false
) where T<:AbstractFloat
_distance(m, T, trait1, point1, trait2, point2)
end
function _distance(::Planar, args...)
_distance(args...)
end
function _distance(m::Spherical, ::Type{T}, trait1::GI.PointTrait, p1, trait2::GI.PointTrait, p2) where T <: AbstractFloat
t = UnitSpherical.UnitSphereFromGeographic()
p1_us = t(p1)
p2_us = t(p2)
dist = UnitSpherical.spherical_distance(p1_us, p2_us)
return T(dist * m.radius)
end
"""
signed_distance(point, geom, ::Type{T} = Float64)::T
Calculates the signed distance from the geometry `geom` to the given point.
Points within `geom` have a negative signed distance, and points outside of
`geom` have a positive signed distance.
- The signed distance from a point to a point, line, linestring, or linear
ring is equal to the distance between the two.
- The signed distance from a point to a polygon is negative if the point is
within the polygon and is positive otherwise. The value of the distance is
the minimum distance from the point to an edge of the polygon. This includes
edges created by holes.
- The signed distance from a point to a multigeometry or a geometry
collection is the minimum signed distance between the point and any of the
sub-geometries.
Result will be of type T, where T is an optional argument with a default value
of Float64.
"""
function signed_distance(
geom1, geom2, ::Type{T} = Float64; threaded=false
) where T<:AbstractFloat
signed_distance(GI.trait(geom1), geom1, GI.trait(geom2), geom2, T; threaded)
end
function signed_distance(
trait1, geom, trait2::GI.PointTrait, point, ::Type{T} = Float64;
threaded=false
) where T<:AbstractFloat
signed_distance(trait2, point, trait1, geom, T; threaded) # Swap order
end
function signed_distance(
trait1::GI.PointTrait, point, trait2, geom, ::Type{T} = Float64;
threaded=false
) where T<:AbstractFloat
applyreduce(min, _DISTANCE_TARGETS, geom; threaded, init=typemax(T)) do g
_signed_distance(T, trait1, point, GI.trait(g), g)
end
endNeeded for method ambiguity
function signed_distance(
trait1::GI.PointTrait, point1, trait2::GI.PointTrait, point2, ::Type{T} = Float64;
threaded=false
) where T<:AbstractFloat
_signed_distance(T, trait1, point1, trait2, point2)
endPoint-Geom (just calls _distance)
function _signed_distance(
::Type{T}, ptrait::GI.PointTrait, point, gtrait::GI.AbstractGeometryTrait, geom
) where T
_distance(T, ptrait, point, gtrait, geom)
endPoint-Polygon
function _signed_distance(::Type{T}, ::GI.PointTrait, point, ::GI.PolygonTrait, geom) where T
min_dist = _distance_polygon(T, point, geom)
return within(point, geom) ? -min_dist : min_distnegative if point is inside polygon
endReturns the Euclidean distance between two points.
Base.@propagate_inbounds _euclid_distance(::Type{T}, p1, p2) where T =
sqrt(_squared_euclid_distance(T, p1, p2))Returns the square of the euclidean distance between two points
Base.@propagate_inbounds _squared_euclid_distance(::Type{T}, p1, p2) where T =
_squared_euclid_distance(
T,
GeoInterface.x(p1), GeoInterface.y(p1),
GeoInterface.x(p2), GeoInterface.y(p2),
)Returns the Euclidean distance between two points given their x and y values.
Base.@propagate_inbounds _euclid_distance(::Type{T}, x1, y1, x2, y2) where T =
sqrt(_squared_euclid_distance(T, x1, y1, x2, y2))Returns the squared Euclidean distance between two points given their x and y values.
Base.@propagate_inbounds _squared_euclid_distance(::Type{T}, x1, y1, x2, y2) where T =
T((x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2)Returns the minimum distance from point p0 to the line defined by endpoints p1 and p2.
_distance_line(::Type{T}, p0, p1, p2) where T =
sqrt(_squared_distance_line(T, p0, p1, p2))Returns the squared minimum distance from point p0 to the line defined by endpoints p1 and p2.
function _squared_distance_line(::Type{T}, p0, p1, p2) where T
x0, y0 = GeoInterface.x(p0), GeoInterface.y(p0)
x1, y1 = GeoInterface.x(p1), GeoInterface.y(p1)
x2, y2 = GeoInterface.x(p2), GeoInterface.y(p2)
xfirst, yfirst, xlast, ylast = x1 < x2 ? (x1, y1, x2, y2) : (x2, y2, x1, y1)
#=
Vectors from first point to last point (v) and from first point to point of
interest (w) to find the projection of w onto v to find closest point
=#
v = (xlast - xfirst, ylast - yfirst)
w = (x0 - xfirst, y0 - yfirst)
c1 = sum(w .* v)
if c1 <= 0 # p0 is closest to first endpoint
return _squared_euclid_distance(T, x0, y0, xfirst, yfirst)
end
c2 = sum(v .* v)
if c2 <= c1 # p0 is closest to last endpoint
return _squared_euclid_distance(T, x0, y0, xlast, ylast)
end
b2 = c1 / c2 # projection fraction
return _squared_euclid_distance(T, x0, y0, xfirst + (b2 * v[1]), yfirst + (b2 * v[2]))
endReturns the minimum distance from the given point to the given curve. If close_curve is true, make sure to include the edge from the first to last point of the curve, even if it isn't explicitly repeated.
function _distance_curve(::Type{T}, point, curve; close_curve = false) where Tsee if linear ring has explicitly repeated last point in coordinates
np = GI.npoint(curve)
first_last_equal = equals(GI.getpoint(curve, 1), GI.getpoint(curve, np))
close_curve &= first_last_equal
np -= first_last_equal ? 1 : 0find minimum distance
min_dist = typemax(T)
p1 = GI.getpoint(curve, close_curve ? np : 1)
for i in (close_curve ? 1 : 2):np
p2 = GI.getpoint(curve, i)
dist = _distance_line(T, point, p1, p2)
min_dist = dist < min_dist ? dist : min_dist
p1 = p2
end
return min_dist
endReturns the minimum distance from the given point to an edge of the given polygon, including from edges created by holes. Assumes polygon isn't filled and treats the exterior and each hole as a linear ring.
function _distance_polygon(::Type{T}, point, poly) where T
min_dist = _distance_curve(T, point, GI.getexterior(poly); close_curve = true)
@inbounds for hole in GI.gethole(poly)
dist = _distance_curve(T, point, hole; close_curve = true)
min_dist = dist < min_dist ? dist : min_dist
end
return min_dist
endThis page was generated using Literate.jl.