Simplify
GeometryOps.simplify Function
simplify(obj; kw...)
simplify(::SimplifyAlg, obj; kw...)Simplify a geometry, feature, feature collection, or nested vectors or a table of these.
RadialDistance, DouglasPeucker, or VisvalingamWhyatt algorithms are available, listed in order of increasing quality but decreasing performance.
PoinTrait and MultiPointTrait are returned unchanged.
The default behaviour is simplify(DouglasPeucker(; kw...), obj). Pass in other SimplifyAlg to use other algorithms.
Keywords
prefilter_alg:SimplifyAlgalgorithm used to pre-filter object before using primary filtering algorithm.threaded:trueorfalse. Whether to use multithreading. Defaults tofalse.crs: The CRS to attach to geometries. Defaults tonothing.calc_extent:trueorfalse. Whether to calculate the extent. Defaults tofalse.
Keywords for DouglasPeucker are allowed when no algorithm is specified:
Keywords
ratio: the fraction of points that should remain aftersimplify. Useful as it will generalise for large collections of objects.number: the number of points that should remain aftersimplify. Less useful for large collections of mixed size objects.tol: the minimum distance a point will be from the line joining its neighboring points.
Example
Simplify a polygon to have six points:
import GeoInterface as GI
import GeometryOps as GO
poly = GI.Polygon([[
[-70.603637, -33.399918],
[-70.614624, -33.395332],
[-70.639343, -33.392466],
[-70.659942, -33.394759],
[-70.683975, -33.404504],
[-70.697021, -33.419406],
[-70.701141, -33.434306],
[-70.700454, -33.446339],
[-70.694274, -33.458369],
[-70.682601, -33.465816],
[-70.668869, -33.472117],
[-70.646209, -33.473835],
[-70.624923, -33.472117],
[-70.609817, -33.468107],
[-70.595397, -33.458369],
[-70.587158, -33.442901],
[-70.587158, -33.426283],
[-70.590591, -33.414248],
[-70.594711, -33.406224],
[-70.603637, -33.399918]]])
simple = GO.simplify(poly; number=6)
GI.npoint(simple)
# output
6GeometryOps.VisvalingamWhyatt Type
VisvalingamWhyatt <: SimplifyAlg
VisvalingamWhyatt(; kw...)Simplifies geometries by removing points below tol distance from the line between its neighboring points.
Keywords
ratio: the fraction of points that should remain aftersimplify. Useful as it will generalise for large collections of objects.number: the number of points that should remain aftersimplify. Less useful for large collections of mixed size objects.tol: the minimum area of a triangle made with a point and its neighboring points.
Note: user input tol is doubled to avoid unnecessary computation in algorithm.
GeometryOps.DouglasPeucker Type
DouglasPeucker <: SimplifyAlg
DouglasPeucker(; number, ratio, tol)Simplifies geometries by removing points below tol distance from the line between its neighboring points.
Keywords
ratio: the fraction of points that should remain aftersimplify. Useful as it will generalise for large collections of objects.number: the number of points that should remain aftersimplify. Less useful for large collections of mixed size objects.tol: the minimum distance a point will be from the line joining its neighboring points.
Note: user input tol is squared to avoid unnecessary computation in algorithm.
GeometryOps.RadialDistance Type
RadialDistance <: SimplifyAlgSimplifies geometries by removing points less than tol distance from the line between its neighboring points.
Keywords
ratio: the fraction of points that should remain aftersimplify. Useful as it will generalise for large collections of objects.number: the number of points that should remain aftersimplify. Less useful for large collections of mixed size objects.tol: the minimum distance between points.
Note: user input tol is squared to avoid unnecessary computation in algorithm.
What is Geometry Simplification?
Geometry simplification reduces the number of points in a geometry while preserving its essential shape. This is usually done by specifying some tolerance.
GeometryOps provides three simplification algorithms: VisvalingamWhyatt, DouglasPeucker, and RadialDistance, listed in order of decreasing quality but increasing performance.
The default algorithm is DouglasPeucker, which is also available through the GEOS extension.
In GeometryOps' algorithms, you can specify tol, number of points, or ratio of points after simplification to points in the input geometry.
The GEOS extension (activated by loading LibGEOS.jl) also allows for GEOS's topology preserving simplification as well as Douglas-Peucker simplification implemented in GEOS. Call this by passing GEOS(; method = :TopologyPreserve) or GEOS(; method = :DouglasPeucker) to the algorithm.
Examples
Here is the simplest example:
using CairoMakie
import GeoInterface as GI
import GeometryOps as GO
original = GI.Polygon([[[-70.603637, -33.399918], [-70.614624, -33.395332], [-70.639343, -33.392466], [-70.659942, -33.394759], [-70.683975, -33.404504], [-70.697021, -33.419406], [-70.701141, -33.434306], [-70.700454, -33.446339], [-70.694274, -33.458369], [-70.682601, -33.465816], [-70.668869, -33.472117], [-70.646209, -33.473835], [-70.624923, -33.472117], [-70.609817, -33.468107], [-70.595397, -33.458369], [-70.587158, -33.442901], [-70.587158, -33.426283], [-70.590591, -33.414248], [-70.594711, -33.406224], [-70.603637, -33.399918]]])
simple = GO.simplify(original; number=6)
f, a, p = poly(original; label = "Original")
poly!(simple; label = "Simplified")
axislegend(a)
f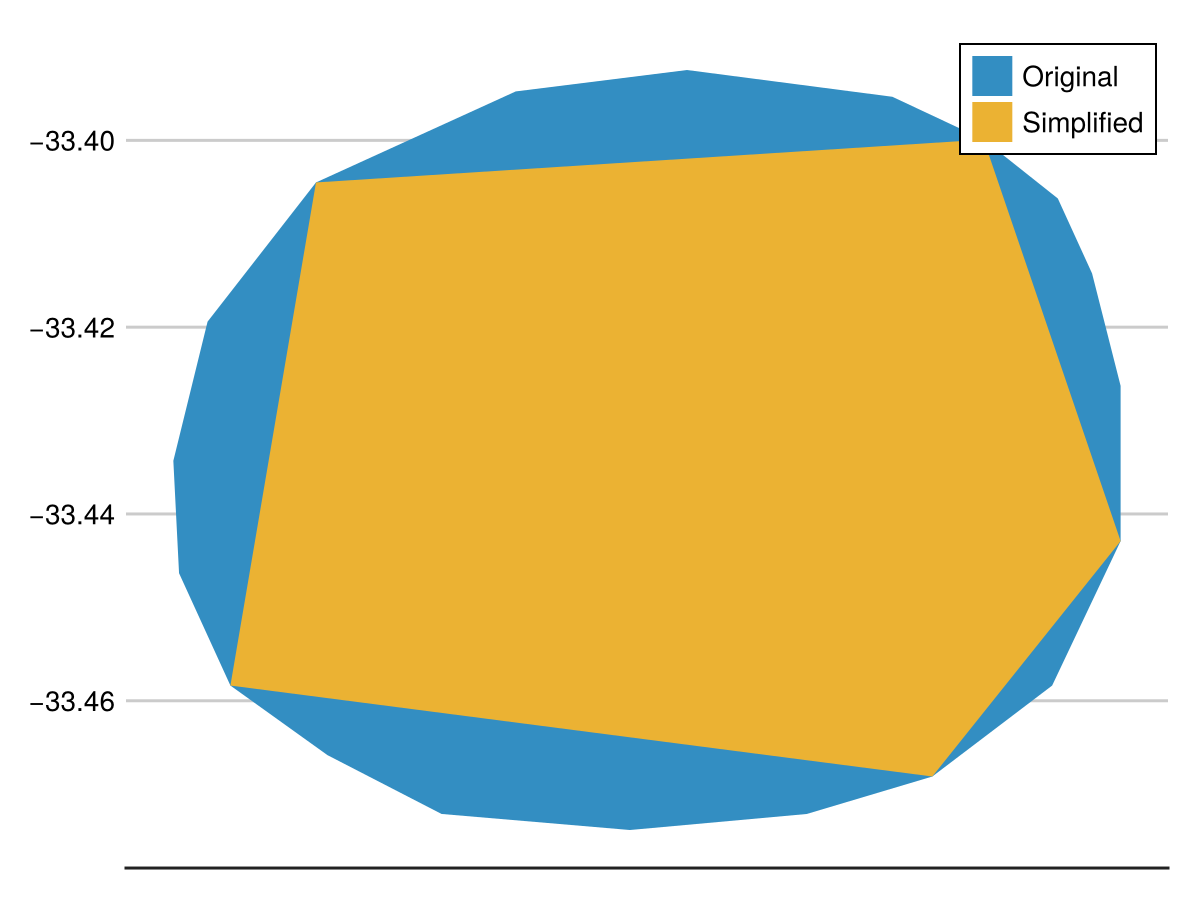
You can also choose the algorithm to use. The algorithm we run here is the same as what we used above:
GO.simplify(GO.DouglasPeucker(number = 6), original)GeoInterface.Wrappers.Polygon{false, false}([GeoInterface.Wrappers.LinearRing([(-70.603637, -33.399918), … (4) … , (-70.603637, -33.399918)])])Benchmarks
Let's benchmark the performance of the algorithms to get a clearer idea of what's going on.
TODO: I had benchmarks but they were not particularly useful. We need to make them better.
export simplify, VisvalingamWhyatt, DouglasPeucker, RadialDistance
const _SIMPLIFY_TARGET = TraitTarget{Union{GI.PolygonTrait, GI.AbstractCurveTrait, GI.MultiPointTrait, GI.PointTrait}}()
const MIN_POINTS = 3
const SIMPLIFY_ALG_KEYWORDS = """
# Keywords
- `ratio`: the fraction of points that should remain after `simplify`.
Useful as it will generalise for large collections of objects.
- `number`: the number of points that should remain after `simplify`.
Less useful for large collections of mixed size objects.
"""
const DOUGLAS_PEUCKER_KEYWORDS = """
$SIMPLIFY_ALG_KEYWORDS
- `tol`: the minimum distance a point will be from the line
joining its neighboring points.
"""
"""
abstract type SimplifyAlg
Abstract type for simplification algorithms.
# API
For now, the algorithm must hold the `number`, `ratio` and `tol` properties.
Simplification algorithm types can hook into the interface by implementing
the `_simplify(trait, alg, geom)` methods for whichever traits are necessary.
"""
abstract type SimplifyAlg end
"""
simplify(obj; kw...)
simplify(::SimplifyAlg, obj; kw...)
Simplify a geometry, feature, feature collection,
or nested vectors or a table of these.
`RadialDistance`, `DouglasPeucker`, or
`VisvalingamWhyatt` algorithms are available,
listed in order of increasing quality but decreasing performance.
`PoinTrait` and `MultiPointTrait` are returned unchanged.
The default behaviour is `simplify(DouglasPeucker(; kw...), obj)`.
Pass in other `SimplifyAlg` to use other algorithms.Keywords
- `prefilter_alg`: `SimplifyAlg` algorithm used to pre-filter object before
using primary filtering algorithm.
$APPLY_KEYWORDS
Keywords for DouglasPeucker are allowed when no algorithm is specified:
$DOUGLAS_PEUCKER_KEYWORDSExample
Simplify a polygon to have six points:
```jldoctest
import GeoInterface as GI
import GeometryOps as GO
poly = GI.Polygon([[
[-70.603637, -33.399918],
[-70.614624, -33.395332],
[-70.639343, -33.392466],
[-70.659942, -33.394759],
[-70.683975, -33.404504],
[-70.697021, -33.419406],
[-70.701141, -33.434306],
[-70.700454, -33.446339],
[-70.694274, -33.458369],
[-70.682601, -33.465816],
[-70.668869, -33.472117],
[-70.646209, -33.473835],
[-70.624923, -33.472117],
[-70.609817, -33.468107],
[-70.595397, -33.458369],
[-70.587158, -33.442901],
[-70.587158, -33.426283],
[-70.590591, -33.414248],
[-70.594711, -33.406224],
[-70.603637, -33.399918]]])
simple = GO.simplify(poly; number=6)
GI.npoint(simple)output
6
```
"""
simplify(alg::SimplifyAlg, data; kw...) = _simplify(alg, data; kw...)Default algorithm is DouglasPeucker
simplify(
data; prefilter_alg = nothing,
calc_extent=false, threaded=false, crs=nothing, kw...,
) = _simplify(DouglasPeucker(; kw...), data; prefilter_alg, calc_extent, threaded, crs)
#= For each algorithm, apply simplification to all curves, multipoints, and
points, reconstructing everything else around them. =#
function _simplify(alg::Union{SimplifyAlg, GEOS}, data; prefilter_alg=nothing, kw...)
simplifier(trait, geom) = _simplify(trait, alg, geom; prefilter_alg)
return apply(WithTrait(simplifier), _SIMPLIFY_TARGET, data; kw...)
end
# For Point and MultiPoint traits we do nothing
_simplify(::GI.PointTrait, alg, geom; kw...) = geom
_simplify(::GI.MultiPointTrait, alg, geom; kw...) = geom
# For curves, rings, and polygon we simplify
function _simplify(
::GI.AbstractCurveTrait, alg, geom;
prefilter_alg, preserve_endpoint = true,
)
points = if isnothing(prefilter_alg)
tuple_points(geom)
else
_simplify(prefilter_alg, tuple_points(geom), preserve_endpoint)
end
return rebuild(geom, _simplify(alg, points, preserve_endpoint))
end
function _simplify(::GI.PolygonTrait, alg, geom; kw...)
# Force treating children as LinearRing
simplifier(g) = _simplify(
GI.LinearRingTrait(), alg, g;
kw..., preserve_endpoint = false,
)
lrs = map(simplifier, GI.getgeom(geom))
return rebuild(geom, lrs)
endSimplify with RadialDistance Algorithm
"""
RadialDistance <: SimplifyAlg
Simplifies geometries by removing points less than
`tol` distance from the line between its neighboring points.
$SIMPLIFY_ALG_KEYWORDS
- `tol`: the minimum distance between points.
Note: user input `tol` is squared to avoid unnecessary computation in algorithm.
"""
@kwdef struct RadialDistance <: SimplifyAlg
number::Union{Int64,Nothing} = nothing
ratio::Union{Float64,Nothing} = nothing
tol::Union{Float64,Nothing} = nothing
function RadialDistance(number, ratio, tol)
_checkargs(number, ratio, tol)square tolerance for reduced computation
tol = isnothing(tol) ? tol : tol^2
new(number, ratio, tol)
end
end
function _simplify(alg::RadialDistance, points::Vector, _)
previous = first(points)
distances = Array{Float64}(undef, length(points))
for i in eachindex(points)
point = points[i]
distances[i] = _squared_euclid_distance(Float64, point, previous)
previous = point
end
# Never remove the end points
distances[begin] = distances[end] = Inf
indices = _get_indices(alg, points, distances)Check there is at least one mid point
if !any(view(indices, firstindex(indices)+1:lastindex(indices)-1))If not use the midpoint of the removed points ?
indices[lastindex(indices) ÷ 2] = true
end
return points[indices]
endSimplify with DouglasPeucker Algorithm
"""
DouglasPeucker <: SimplifyAlg
DouglasPeucker(; number, ratio, tol)
Simplifies geometries by removing points below `tol`
distance from the line between its neighboring points.
$DOUGLAS_PEUCKER_KEYWORDS
Note: user input `tol` is squared to avoid unnecessary computation in algorithm.
"""
@kwdef struct DouglasPeucker <: SimplifyAlg
number::Union{Int64,Nothing} = nothing
ratio::Union{Float64,Nothing} = nothing
tol::Union{Float64,Nothing} = nothing
function DouglasPeucker(number, ratio, tol)
_checkargs(number, ratio, tol)square tolerance for reduced computation
tol = isnothing(tol) ? tol : tol^2
return new(number, ratio, tol)
end
end
#= Simplify using the DouglasPeucker algorithm - nice gif of process on wikipedia:
(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ramer-Douglas-Peucker_algorithm). =#
function _simplify(alg::DouglasPeucker, points::Vector, preserve_endpoint)
npoints = length(points)
npoints <= MIN_POINTS && return pointsDetermine stopping criteria
max_points = if !isnothing(alg.tol)
npoints
else
npts = !isnothing(alg.number) ? alg.number : max(3, round(Int, alg.ratio * npoints))
npts ≥ npoints && return points
npts
end
max_tol = !isnothing(alg.tol) ? alg.tol : zero(Float64)Set up queue
queue = Vector{Tuple{Int, Int, Int, Float64}}()
queue_idx, queue_dist = 0, zero(Float64)
len_queue = 0Set up results vector
results = Vector{Int}(undef, max_points + (preserve_endpoint ? 0 : 1))
results[1], results[2] = 1, npointsLoop through points until stopping criteria are fulfilled
i = 2 # already have first and last point added
start_idx, end_idx = 1, npoints
max_idx, max_dist = _find_max_squared_dist(points, start_idx, end_idx)
while i ≤ min(MIN_POINTS + 1, max_points) || (i < max_points && max_dist > max_tol)Add next point to results
i += 1
results[i] = max_idxDetermine which point to add next by checking left and right of point
left_idx, left_dist = _find_max_squared_dist(points, start_idx, max_idx)
right_idx, right_dist = _find_max_squared_dist(points, max_idx, end_idx)
left_vals = (start_idx, left_idx, max_idx, left_dist)
right_vals = (max_idx, right_idx, end_idx, right_dist)Add and remove values from queue
if queue_dist > left_dist && queue_dist > right_distValue in queue is next value to add to results
start_idx, max_idx, end_idx, max_dist = queue[queue_idx]Add left and/or right values to queue or delete used queue value
if left_dist > 0
queue[queue_idx] = left_vals
if right_dist > 0
push!(queue, right_vals)
len_queue += 1
end
elseif right_dist > 0
queue[queue_idx] = right_vals
else
deleteat!(queue, queue_idx)
len_queue -= 1
endDetermine new maximum queue value
queue_dist, queue_idx = !isempty(queue) ?
findmax(x -> x[4], queue) : (zero(Float64), 0)
elseif left_dist > right_dist # use left value as next value to add to results
push!(queue, right_vals) # add right value to queue
len_queue += 1
if right_dist > queue_dist
queue_dist = right_dist
queue_idx = len_queue
end
start_idx, max_idx, end_idx, max_dist = left_vals
else # use right value as next value to add to results
push!(queue, left_vals) # add left value to queue
len_queue += 1
if left_dist > queue_dist
queue_dist = left_dist
queue_idx = len_queue
end
start_idx, max_idx, end_idx, max_dist = right_vals
end
end
sorted_results = sort!(@view results[1:i])
if !preserve_endpoint && i > 3Check start/endpoint distance to other points to see if it meets criteria
pre_pt, post_pt = points[sorted_results[end - 1]], points[sorted_results[2]]
endpt_dist = _squared_distance_line(Float64, points[1], pre_pt, post_pt)
if !isnothing(alg.tol)Remove start point and replace with second point
if endpt_dist < max_tol
results[i] = results[2]
sorted_results = @view results[2:i]
end
elseRemove start point and add point with maximum distance still remaining
if endpt_dist < max_dist
insert!(results, searchsortedfirst(sorted_results, max_idx), max_idx)
results[i+1] = results[2]
sorted_results = @view results[2:i+1]
end
end
end
return points[sorted_results]
end
#= find maximum distance of any point between the start_idx and end_idx to the line formed
by connecting the points at start_idx and end_idx. Note that the first index of maximum
value will be used, which might cause differences in results from other algorithms.=#
function _find_max_squared_dist(points, start_idx, end_idx)
max_idx = start_idx
max_dist = zero(Float64)
for i in (start_idx + 1):(end_idx - 1)
d = _squared_distance_line(Float64, points[i], points[start_idx], points[end_idx])
if d > max_dist
max_dist = d
max_idx = i
end
end
return max_idx, max_dist
endSimplify with VisvalingamWhyatt Algorithm
"""
VisvalingamWhyatt <: SimplifyAlg
VisvalingamWhyatt(; kw...)
Simplifies geometries by removing points below `tol`
distance from the line between its neighboring points.
$SIMPLIFY_ALG_KEYWORDS
- `tol`: the minimum area of a triangle made with a point and
its neighboring points.
Note: user input `tol` is doubled to avoid unnecessary computation in algorithm.
"""
@kwdef struct VisvalingamWhyatt <: SimplifyAlg
number::Union{Int,Nothing} = nothing
ratio::Union{Float64,Nothing} = nothing
tol::Union{Float64,Nothing} = nothing
function VisvalingamWhyatt(number, ratio, tol)
_checkargs(number, ratio, tol)double tolerance for reduced computation
tol = isnothing(tol) ? tol : tol*2
return new(number, ratio, tol)
end
end
function _simplify(alg::VisvalingamWhyatt, points::Vector, _)
length(points) <= MIN_POINTS && return points
areas = _build_tolerances(_triangle_double_area, points)
return points[_get_indices(alg, points, areas)]
endCalculates double the area of a triangle given its vertices
_triangle_double_area(p1, p2, p3) =
abs(p1[1] * (p2[2] - p3[2]) + p2[1] * (p3[2] - p1[2]) + p3[1] * (p1[2] - p2[2]))Shared utils
function _build_tolerances(f, points)
nmax = length(points)
real_tolerances = _flat_tolerances(f, points)
tolerances = copy(real_tolerances)
i = [n for n in 1:nmax]
this_tolerance, min_vert = findmin(tolerances)
_remove!(tolerances, min_vert)
deleteat!(i, min_vert)
while this_tolerance < Inf
skip = false
if min_vert < length(i)
right_tolerance = f(
points[i[min_vert - 1]],
points[i[min_vert]],
points[i[min_vert + 1]],
)
if right_tolerance <= this_tolerance
right_tolerance = this_tolerance
skip = min_vert == 1
end
real_tolerances[i[min_vert]] = right_tolerance
tolerances[min_vert] = right_tolerance
end
if min_vert > 2
left_tolerance = f(
points[i[min_vert - 2]],
points[i[min_vert - 1]],
points[i[min_vert]],
)
if left_tolerance <= this_tolerance
left_tolerance = this_tolerance
skip = min_vert == 2
end
real_tolerances[i[min_vert - 1]] = left_tolerance
tolerances[min_vert - 1] = left_tolerance
end
if !skip
min_vert = argmin(tolerances)
end
deleteat!(i, min_vert)
this_tolerance = tolerances[min_vert]
_remove!(tolerances, min_vert)
end
return real_tolerances
end
function tuple_points(geom)
points = Array{Tuple{Float64,Float64}}(undef, GI.npoint(geom))
for (i, p) in enumerate(GI.getpoint(geom))
points[i] = (GI.x(p), GI.y(p))
end
return points
end
function _get_indices(alg, points, tolerances)
# This assumes that `alg` has the properties
# `tol`, `number`, and `ratio` available...
tol = alg.tol
number = alg.number
ratio = alg.ratio
return if !isnothing(tol)
_tol_indices(alg.tol::Float64, points, tolerances)
elseif !isnothing(number)
_number_indices(alg.number::Int64, points, tolerances)
else
_ratio_indices(alg.ratio::Float64, points, tolerances)
end
end
function _tol_indices(tol, points, tolerances)
tolerances .>= tol
end
function _number_indices(n, points, tolerances)
tol = partialsort(tolerances, length(points) - n + 1)
bit_indices = _tol_indices(tol, points, tolerances)
nselected = sum(bit_indices)
# If there are multiple values exactly at `tol` we will get
# the wrong output length. So we need to remove some.
while nselected > n
min_tol = Inf
min_i = 0
for i in eachindex(bit_indices)
bit_indices[i] || continue
if tolerances[i] < min_tol
min_tol = tolerances[i]
min_i = i
end
end
nselected -= 1
bit_indices[min_i] = false
end
return bit_indices
end
function _ratio_indices(r, points, tolerances)
n = max(3, round(Int, r * length(points)))
return _number_indices(n, points, tolerances)
end
function _flat_tolerances(f, points)::Vector{Float64}
result = Vector{Float64}(undef, length(points))
result[1] = result[end] = Inf
for i in 2:length(result) - 1
result[i] = f(points[i-1], points[i], points[i+1])
end
return result
end
function _remove!(s, i)
for j in i:lastindex(s)-1
s[j] = s[j+1]
end
endCheck SimplifyAlgs inputs to make sure they are valid for below algorithms
function _checkargs(number, ratio, tol)
count(isnothing, (number, ratio, tol)) == 2 ||
error("Must provide one of `number`, `ratio` or `tol` keywords")
if !isnothing(number)
if number < MIN_POINTS
error("`number` must be $MIN_POINTS or larger. Got $number")
end
elseif !isnothing(ratio)
if ratio <= 0 || ratio > 1
error("`ratio` must be 0 < ratio <= 1. Got $ratio")
end
else # !isnothing(tol)
if tol ≤ 0
error("`tol` must be a positive number. Got $tol")
end
end
return nothing
endThis page was generated using Literate.jl.