Smooth
Geometry smoothing is meant to make shapes more aesthetically pleasing, usually by rounding out rough edges and corners.
You can do this by the smooth function, which uses the Chaikin algorithm by default.
Example
julia
using CairoMakie
import GeoInterface as GI, GeometryOps as GO
line = GI.LineString([(0.0, 0.0), (1.0, 1.0), (2.0, 0.0)])
smoothed = GO.smooth(line)
smoothed_2 = GO.smooth(line; iterations=2)
f, a, p = lines(line; label = "line")
lines!(a, smoothed; label = "smooth(line; iterations=1)")
lines!(a, smoothed_2; label = "smooth(line; iterations=2)")
axislegend(a)
f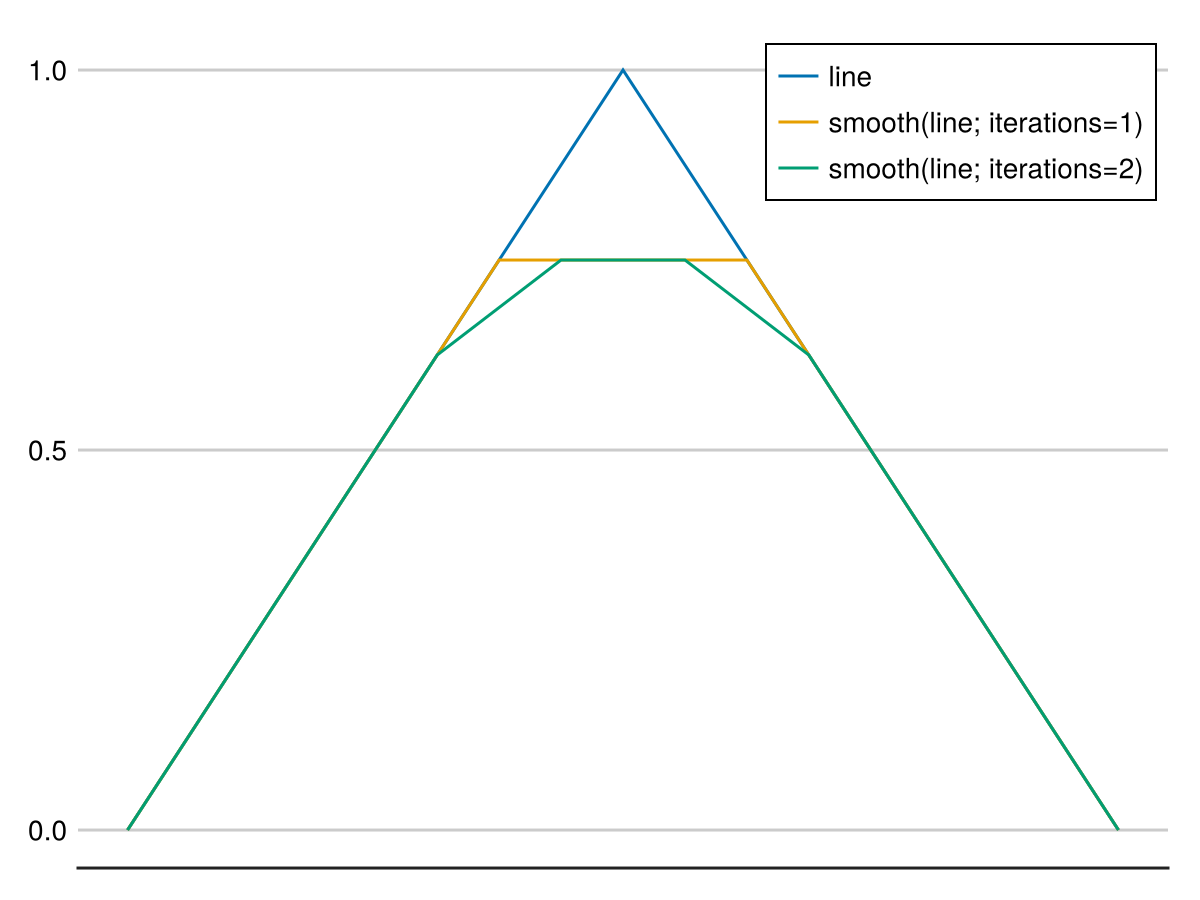
Smoothing also works on the Spherical manifold, similarly to the planar manifold (default):
@example
using CairoMakie
import GeoInterface as GI, GeometryOps as GO
line = GI.LineString([(0.0, 0.0), (1.0, 1.0), (2.0, 0.0)])
smoothed = GO.smooth(GO.Spherical(), line) |> x -> GO.transform(GO.UnitSpherical.GeographicFromUnitSpherical(), x)
smoothed_2 = GO.smooth(GO.Spherical(), line; iterations=2) |> x -> GO.transform(GO.UnitSpherical.GeographicFromUnitSpherical(), x)
f, a, p = lines(line; label = "Original", axis = (; title = "Spherical smoothing"))
lines!(a, smoothed; label = "1 iteration")
lines!(a, smoothed_2; label = "2 iterations")
axislegend(a)
fjulia
"""
Chaikin(; iterations=1, manifold=Planar())
Smooths geometries using Chaikin's corner-cutting algorithm [^1].
This algorithm "slices" off every corner of the geometry to smooth it out,
equivalent to a sequence of quadratic Bezier curves.
# Keywords
- `iterations`: the number of times to apply the algorithm.
- `manifold`: the `Manifold` to smooth the geometry on. Currently, `Planar` and `Spherical` are supported.Extended help
julia
The algorithm is very simple; for each corner of the line (a -> b -> c),
insert two new points and remove b, such that `a -> b -> c` becomes
`a -> q -> r -> c`, where `q` and `r` are the new points such that:
```math
q = 3/4 * b + 1/4 * a
r = 3/4 * b + 1/4 * c
```
In practice the replacement happens on the level of each edge.
# References
[^1]: Chaikin, G. An algorithm for high speed curve generation. Computer Graphics and Image Processing 3 (1974), 346-349
"""
@kwdef struct Chaikin{M} <: Algorithm{M}
manifold::M = Planar()
iterations::Int = 1
end
"""
smooth(alg::Algorithm, geom)
smooth(geom; kw...)
Smooths a geometry using the provided algorithm.
The default algorithm is `Chaikin()`, which can be used on the spherical or planar manifolds.
"""
smooth(geom; kw...) = smooth(Chaikin(; kw...), geom)
smooth(m::Manifold, geom; kw...) = smooth(Chaikin(; manifold=m, kw...), geom)
function smooth(alg::Algorithm, geom; kw...)
_smooth_function(trait, geom) = _smooth(alg, trait, geom)
return apply(
WithTrait(_smooth_function),
TraitTarget{Union{GI.AbstractCurveTrait,GI.MultiPointTrait,GI.PointTrait}}(),
geom;
kw...
)
end
_smooth(alg, ::GI.PointTrait, geom) = geom
_smooth(alg, ::GI.MultiPointTrait, geom) = geom
function _smooth(alg::Chaikin{<: Planar}, trait::Trait, geom) where {Trait <: Union{GI.LineStringTrait,GI.LinearRingTrait}}
isring = Trait <: GI.LinearRingTrait
points = tuple_points(geom)
if isring && first(points) != last(points)
push!(points, first(points))
end
smoothed_points = _chaikin_smooth(alg.manifold, points, alg.iterations, isring)
return rebuild(geom, smoothed_points)
end
function _smooth(alg::Chaikin{<: M}, trait::Trait, geom) where {M <: Spherical, Trait <: Union{GI.LineStringTrait,GI.LinearRingTrait}}
isring = Trait <: GI.LinearRingTrait
points = apply(UnitSphereFromGeographic(), GI.PointTrait(), geom).geom
if isring && first(points) != last(points)
push!(points, first(points))
end
smoothed_points = _chaikin_smooth(alg.manifold, points, alg.iterations, isring)
return rebuild(geom, smoothed_points)
end
function _chaikin_smooth(manifold::M, points::Vector{P}, iterations::Int, isring::Bool) where {M <: Manifold, P}points is expected to be a vector of points
julia
smoothed_points = points
for itr in 1:iterations
num_points = length(smoothed_points)
if isring
n = 1
new_points = Vector{P}(undef, num_points * 2 - 1)
else
n = 2Need to add the first point
julia
new_points = Vector{P}(undef, num_points * 2)
new_points[begin] = smoothed_points[begin]
new_points[end] = smoothed_points[end]
endfill!(new_points, (P <: NTuple{2, Float64} ? (-9999.0, -9999.0) : UnitSphericalPoint(-9999.0, -9999.0, -9999.0)))
julia
for i in eachindex(smoothed_points)[begin:end-1]
p1 = smoothed_points[i]
p2 = smoothed_points[i+1]
_add_smoothed_points!(manifold, new_points, p1, p2, n)
n += 2
end
if isring # Close it
new_points[end] = new_points[begin]
end
smoothed_points = new_points
end
return smoothed_points
end
function _add_smoothed_points!(::Planar, new_points, p1, p2, n)
q_x = 0.75 * GI.x(p1) + 0.25 * GI.x(p2)
q_y = 0.75 * GI.y(p1) + 0.25 * GI.y(p2)
r_x = 0.25 * GI.x(p1) + 0.75 * GI.x(p2)
r_y = 0.25 * GI.y(p1) + 0.75 * GI.y(p2)
new_points[n] = (q_x, q_y)
new_points[n+1] = (r_x, r_y)
endFor spherical points, we can simply slerp.
julia
function _add_smoothed_points!(::Spherical, new_points, p1, p2, n)
q = slerp(p1, p2, 0.25)
r = slerp(p1, p2, 0.75)
new_points[n] = q
new_points[n+1] = r
endThis page was generated using Literate.jl.